Accrual accounting is mandatory for any business grossing over $25 million a year. When you choose this method, you can stick with the same accounting procedures as your business grows, as it is designed to work with any size business. All accruals fall into one of two categories—either revenue or expense accrual. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Despite its shortcomings, accruals remain a valuable and essential tool for investors, especially when used alongside other performance metrics. This will result in overstating assets (because more has been earned) and understating liabilities/stockholders’ equity (since less is owed).
How Does It Differ From Cash Accounting?
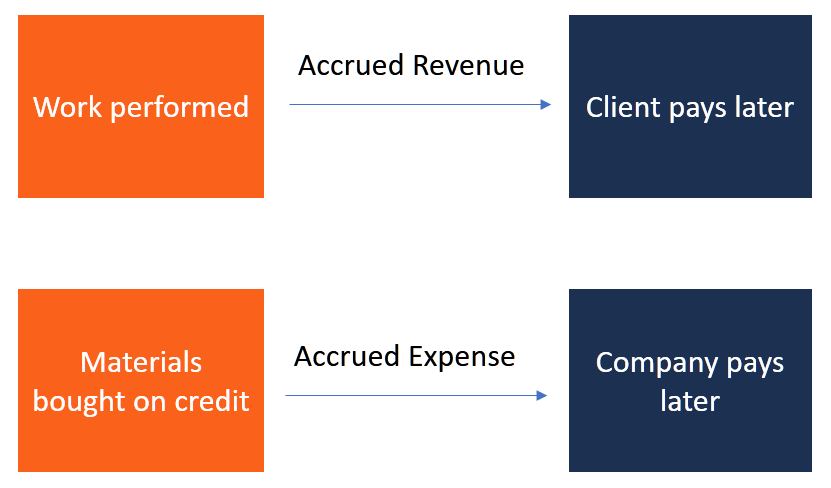
- Similarly, expenses are recognized when they are incurred, even if the payment is not made until a later date.
- This means you already paid for the goods or services that you’re yet to receive.
- An accrual is an accounting adjustment used to track and record revenues that have been earned but not received, or expenses that have been incurred but not paid.
- Accrual accounting makes it easy to get an accurate picture of your company’s financial health, as you can not only see the money you’ve earned but get the full picture of accrued liabilities and revenue.
Salaries are accrued whenever a workweek does not neatly correspond with monthly financial reports and payroll. If employees have to work on January 29, 30, or 31, those workdays still count toward the January operating expenses. Current payroll has not yet accounted for those salary expenses, so an accrued salary account is used. Accrual accounting is always required for companies that carry inventory or make sales on credit, regardless of the company size or revenue.
Which of the following is true about accrual-basis accounting?

A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
What is the purpose of accrual accounting?
As a result, more companies are looking for highly skilled financial accounting professionals, well-versed in this method. Here’s an overview of the accrual accounting method and why so many organizations rely on it. The three accounting methods are cash basis of accounting, accrual basis of accounting, and a hybrid of the two called modified cash basis of accounting. Accrual records payments and receipts when services or good are provided or debt is incurred.
What Are Accruals? How Accrual Accounting Works, With Examples
The accrual method looks at transactions but does not account for actual cash flows within the business. For example, your income statement might show sales revenue, but the client may take months to pay their invoice. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) 2Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service. Notes that if you use the accrual method, you generally report income in the tax year you earn it and deduct expenses in the tax year you incur them, regardless of when payments are received and made. Interest, taxes and other payments sometimes need to be put into accrued entries whenever unpaid obligations should be recognized in the financial statements. Otherwise, the operating expenses for a certain period might be understated, which would result in net income being overstated.
If the company receives an electric bill for $1,700, under the cash method, the amount is not recorded until the company actually pays the bill. However, under the accrual method, the $1,700 is recorded as an expense the day the company receives the bill. For investors, it’s important to understand the impact of both methods when making investment decisions.
It takes into account things like revenue for services or if you have inventory that’s been exchanged. Accruals are earned revenues or expenses incurred that impact a business’s net income. However, the money for these revenues or expenses haven’t yet gone out or come in. An accrued expense refers to any liabilities, losses, or ongoing accounts payable that have not yet been recorded. The basic rule of accrual accounting is to record transactions when they happen instead of when you receive or deliver payment. In this post, we’ll go over what you need to know about the accrual method of accounting, including its benefits, how it compares to cash accounting, and if it’s right for your business.
The statement of cash flows reports a company’s cash inflows and outflows for a specific period. While accrual accounting does not directly impact the statement of cash flows, it can indirectly affect it by influencing the timing of cash flows. Accrued assets and liabilities are those that have been accruals definition earned or incurred but have not yet been recorded in the accounting system. For example, a company may have earned interest on an investment, but the interest has not yet been received. Similarly, a company may have incurred interest expense on a loan, but the payment has not yet been made.
Interest in a savings account, for example, accrues over time, such that the total amount in that account grows. The term accrue is often related to accrual accounting, which has become the standard accounting practice for most companies. The accounting journal is the first entry in the accounting process where transactions are recorded as they occur.
